What Is Insomnia?
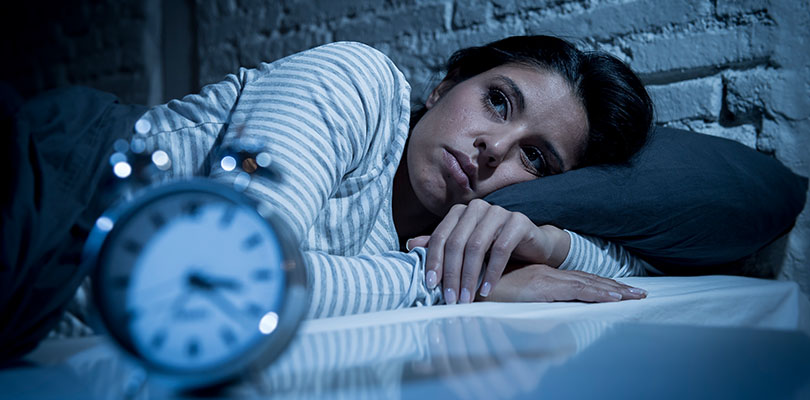
The presence of insomnia can wreak havoc in anyone’s life. Even though the condition affects more than one-third of adults, the condition is well-known but not well-understood by the public and experts alike.
Knowing the condition allows you to understand yourself. It can also help you plan treatment with the goal of good sleep in mind.
Insomnia Overview and Symptoms
Insomnia is a sleep disorder. People may experience:
- Need a long time to fall asleep at night
- Wake up too early in the morning
- Sleep in short bursts rather than unbroken stretches
- Spend a lot of the night awake
- Feel tired and unrested in the morning
Because of these effects, people with insomnia get too little sleep, and the rest they do get is poor-quality sleep. Without achieving good quality and quantity of sleep, you might struggle to focus or pay attention during the day. With time, this condition can result in depression, anxiety, and increased irritability.
The condition carries other risks as well as about 20 percent of all serious car crash injuries being due to insomnia or drivers being tired. Older women with this condition are more likely to fall and become injured.
Types of Insomnia
You might not realize insomnia is not a one-size-fits-all condition. There are four different categories of this condition is based on the causes and duration of symptoms.
The different types are:
- Acute
- Chronic
- Secondary
- Primary
Someone can have primary insomnia that is acute or chronic, or they can have secondary insomnia that is acute or chronic.
The first categories are based on how long the condition lasts for.
- Acute – symptoms lasting for days or weeks
- Chronic – symptoms lasting for months or years
The second category is based on the source of the symptoms.
Secondary Insomnia
Another problem causes secondary insomnia, so insomnia is not the problem, it is a symptom of another problem. There are physical, neurological, and psychological causes.
- Physical:
- Pain – arthritis, and headaches
- Respiration issues from asthma and heart failure
- Thyroid problems
- Gastrointestinal issues like heartburn
- Menopause
- Sleep apnea
- Restless leg syndrome
- Neurological:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Psychological:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Along with the above causes, prescription and over-the-counter medications trigger secondary insomnia. Many medications, including asthma and heart drugs, carry sleeplessness as a side effect.
Primary Insomnia
The final type of the condition is primary insomnia. Primary insomnia occurs when no other situation causes the issues with poor sleep.
Although the condition is not well-understand, experts believe many issues produce primary insomnia with options including a significant emotional strain or long-term stressor. Even life changes like increased travel, moving to a new home, having a baby, or a change in work shift could cause it.
Primary insomnia is usually chronic and lasts for a month or more. You might think your sleep patterns will return to normal when the travel, shift change, or strain ends, but it has a way of lasting long after the stress ends.
Receiving proper treatment can help most people living with bipolar disorder. Discover the different bipolar treatment options here.
Risk Factors for Insomnia
This condition can affect anyone, but you have a higher chance of having the condition if you:
- Are female
- Are an older adult
- Are African American
- Have high stress
- Have a lower income
- Work night shift
- Travel across multiple time zones
- Have a sedentary lifestyle
Treatment for Insomnia
Getting a proper diagnosis is important for your condition. From there, your focus can be on the most effective treatment for your needs.
Medications are one type of treatment a doctor could recommend. Using a prescription sleeping pill short-term could reestablish a healthy sleeping routine.
People interested in natural remedies for the condition may try supplements like melatonin or L-tryptophan. Valerian teas help many find recuperative sleep.
Lifestyle Changes
People who need help beyond medications should consider lifestyle changes to improve their sleep. Start by establishing a simple routine around going to bed with no electronics, bright lights, or major activity for an hour before your intended bedtime.
Create a calm, quiet, and comfortable sleeping environment in a dark room. So, if you struggle to fall asleep, get out of bed for 20 minutes to read in another room before returning to bed.
Your actions and what you consume at night will impact your sleep levels so avoid caffeine, tobacco, physical activity, and alcohol before bed. Some think alcohol improves sleep, but it produces sleep that is less restful, which leaves you feeling tired in the morning.
Therapy
If lifestyle changes are not enough, therapy might solve your sleeping issues. A specific therapy called cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) investigates your thoughts and actions that maintain sleeplessness. By retraining your thoughts and modifying your behaviors with the aid of a professional, you can tackle the condition.
A therapist can teach you relaxation techniques and biofeedback to notice and control your body. With relaxed muscles, slowed breathing, and reduced heart rate, you can fall asleep and stay asleep.
CBT treatment for this condition can be accomplished in a weekly group or individual sessions over the course of two or three months.
Everyone struggles with sleep, but this condition is something different. The condition does not have to wreck your sleep for long, though. With proper diagnosis and treatment, you can say goodnight to insomnia.