What You Need to Know About Hemorrhoids
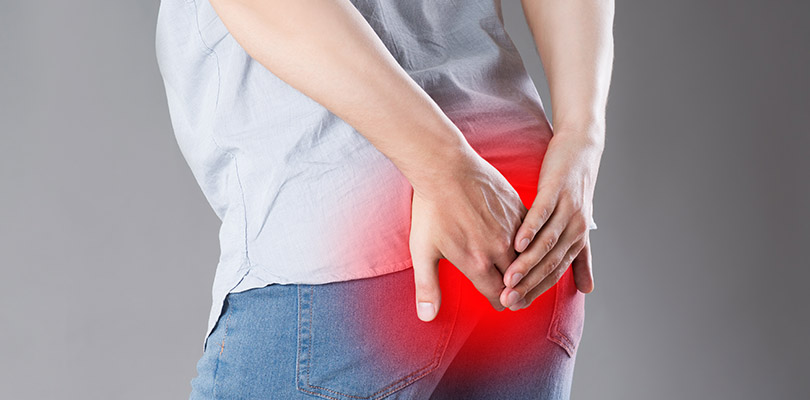
Hemorrhoids are an embarrassing but common problem which affects millions of adults each year. Although hemorrhoids are rarely dangerous, they can have a major impact on the sufferer’s quality of life. Therefore, it is always important to get a hemorrhoid checked out to avoid them becoming worse and rule out more serious underlying conditions.
What Are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are bundles of blood vessels, connective tissue, and smooth muscle which line the anal canal. Everybody has them, even healthy people. When these bundles become problematic, the official term is ‘symptomatic hemorrhoid disease.’ However, the name of the condition is usually shortened to ‘hemorrhoids,’ also known as ‘piles.’
Symptoms arise when the blood vessels in a hemorrhoid become enlarged which can cause them to protrude from the anus. This can cause problems such as bleeding and pain, although many people with this condition may never experience any symptoms.
What Causes Hemorrhoids?
A hemorrhoid is usually a result of excessive pressure on the blood vessels in the rectum and anus. Some common causes of hemorrhoids may include:
- Constipation
- Pregnancy
- Being overweight
- Straining while coughing or lifting
- Anal sex
You may also be more likely to develop piles if you are aged 45–65, suffer from chronic diarrhea, frequently sit for long periods, or have a family history of the condition.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Although some people with piles do not have any symptoms, for others the condition can be both uncomfortable and worrying. One of the most alarming symptoms of a hemorrhoid is bleeding from the anus. This can be noticed following a bowel movement and the blood is usually bright red.
Other symptoms include:
- Red, sore skin or itching around the anus
- Lumps or swellings around the anus
- Passing mucus after emptying the bowels
If you are experiencing hemorrhoid symptoms for the first time, it is important to see a doctor, especially if your bowel habits have also changed suddenly.
Types of Hemorrhoids
There are two main types of hemorrhoids, internal and external. As the names suggest, an internal hemorrhoid is located inside the rectum, while an external hemorrhoid is found around the anus.
An Internal hemorrhoid is usually painless, but sometimes they protrude out of the anus, a problem known as a prolapsed hemorrhoid.
In addition, hemorrhoids can become thrombosed or strangulated. A thrombosed hemorrhoid occurs when blood clots form inside the hemorrhoids, causing swelling and painful lumps.
A strangulated hemorrhoid occurs when the blood supply to an internal hemorrhoid is cut off, another process which can be extremely painful.
Many parents face the issue of their kids wetting the bed. Read on to learn why child bed-wetting happens and how to deal with it.
Treatment of Hemorrhoids
In many cases, piles will disappear on their own and do not require any treatment. However, there are many options for more severe hemorrhoids including topical preparations, non-surgical procedures, and in extreme cases, surgery.
Topical Preparations
For a mildly symptomatic hemorrhoid, you can purchase a variety of over-the-counter remedies including creams, ointments, and suppositories.
These preparations work to soothe itching and pain while the piles heal. These products are generally safe, but should only be used for up to a week at a time. Using them for longer than this can irritate the skin around the anus and make matters worse in the long run.
Non-Surgical Procedures
For more serious piles, there are a variety of non-surgical procedures.
Rubber band ligation involves fixing an elastic band around the base of a hemorrhoid to cut off the blood supply. This causes the tissue to die and fall off. Although this usually happens within a few days, it can take several weeks to heal fully.
Sclerotherapy is another non-surgical procedure for hemorrhoids. It involves injecting the piles with a substance which causes them to harden and shrink. The whole process usually takes four to six weeks.
Infrared coagulation and electrocoagulation are both techniques which cause the blood in hemorrhoids to thicken and piles to shrink. The procedure is considered safe, although not as effective as rubber band ligation.
Surgery
For very severe hemorrhoids, surgery may be necessary. Some common procedures include hemorrhoidectomy, artery ligation, and stapling. These procedures are carried out under general anesthetic and have a healing time of several weeks.
Other Treatments
Other treatments for hemorrhoids include lifestyle changes such as eating more fiber (to avoid constipation) and using home treatments such as a sitz bath.
A sitz bath is a basin which is designed to fit over your toilet bowl and allows you to easily soak your piles in soothing, warm water. A sitz bath is a good investment if you suffer from this, but you can also use a regular bathtub filled with plain, warm (not hot) water.
Prevention of Hemorrhoids
You can reduce your risk of hemorrhoids by making some simple changes to your diet and lifestyle.
First and foremost, it is essential that you avoid constipation. This means eating a diet which is high in fiber from fruit, vegetables, whole grain cereals, and legumes. Ask your physician about fiber supplements if this is not possible.
Staying hydrated by drinking enough water and avoiding alcohol and caffeine can also help to keep the stools soft, making bowel movements easier.
When you need to empty your bowels, try and do this straight away. If you delay a bowel movement, more water is absorbed back into your body, making the stools hard and dry and potentially leading to constipation.
Another common cause of constipation is medication. Many drugs cause constipation as a side effect, especially strong painkillers such as opioids. Check the side effects of any medication you take and talk to your doctor about alternatives if necessary.
Make bowel movements easier by putting your feet up on a low stool or similar while you sit on the toilet. Always use moist toilet paper and remember to wipe gently!
Maintaining a healthy weight is another way to reduce pressure on your bowels and prevent hemorrhoids. The best way to do this is by combining a balanced diet with regular exercise. This will also benefit your digestion and help to prevent constipation, allowing you to reduce your risk of hemorrhoids in multiple ways.