Vaping vs. Smoking: Is Vaping Better for Your Health than Smoking?
There has been an explosion in the growth of vaping since the late 2000s and the trend continues to rise. There is a lot to learn about vaping, including how it works and what exactly it is.
Given the research and history of smoking, there is an assumption that vaping must be better for you than smoking cigarettes. Is that true?
What Is Vaping?
Electronic cigarettes were patented in the 1960s, and it’s been full steam ahead ever since.
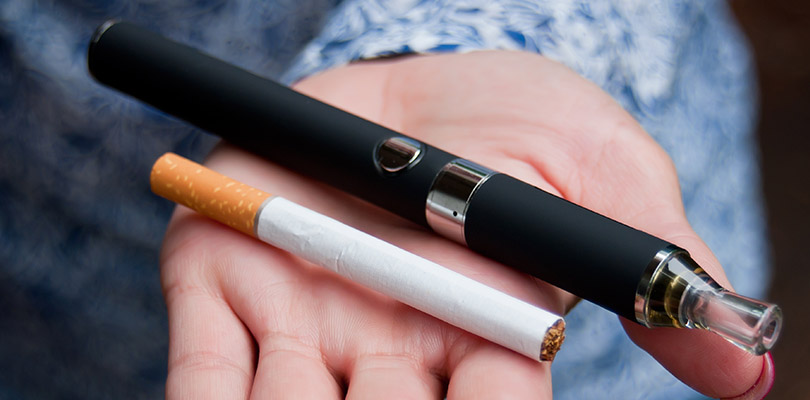
Bucking the trend of smoking tobacco cigarettes, people use an electric device called a vaporizer to inhale the device’s by-product. Vaping can come in the form of e-cigarettes, vape pens, and electric or electronic hookahs, which all create vapor.
Vapor is a substance suspended/diffused in the air which originally started as a liquid or solid form. When it comes to inhaling the vapor, “sipping” is recommended; you take slow, smooth drag from the vaporizer rather than a strong pull into your lungs.
Visually, the exhaled clouds of vapor resemble plumes of smoke, but vapor disperses much quicker.
The Vaporizer
The vaporizer is made up of a battery, main console, cartridge, and atomizer (or cartomizer). The power from the battery heats the elements in the atomizer, which contacts the vaping material.
Common vaping materials are waxy concentrates, dry herbs, and e-liquids. The contact from the atomizer is what turns the vaping material into vapor, which can then be inhaled.
Different vaporizers are used for different materials, so if you vape, be sure to use the right device with the proper vaping material. Vaporizers for e-liquids have a cartridge, and a dry herb vaporizer has a heating chamber.
Multipurpose vaporizers are good for different materials, and you just need to remember to switch out the cartridges to accommodate different materials.
E-liquids
E-liquids, or e-juice, is the most common material used in vaporizers. This fluid also acts as a coolant for the atomizer and keeps the temperature between 140 to 158 Fahrenheit (or 60 to 70 degrees Celsius). Controlling the heat temperature creates a vapor with minimal combustion which means you inhale less smoke.
E-liquids are made of a propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin base (chemicals to vaporize the nicotine), a variety of flavorings, other additives, and may or may not contain nicotine. Some vendors allow you to create your own flavor by mixing flavors they have available.
E-juice differs between manufacturers and doesn’t have much regulation around its additives, which has raised some questions about regulation of vaporizers.
What is Smoking (Traditional Cigarettes)?
Cigarettes were developed in the 1800s. Smoking cigarettes are the most popular form of using tobacco. The heat from the fire source causes the cigarette substance to change from a solid state to a vapor, and this change in states releases the nicotine.
By smoking tobacco, nicotine hits the bloodstream (through the lungs) and gets transported to the brain. Once the nicotine reaches the brain, it stimulates the adrenal glands which release epinephrine (also known as adrenaline).
This feel-good sensation from the nicotine is what triggers the craving and perceived need for more cigarettes when the stimulation wears off. Cigarettes themselves contain about 600 ingredients, and they create more than 7000 chemicals when they are burned.
The Difference Between Vaping vs. Smoking
With the way that vaporizers work, e-liquids contain less nicotine than normal tobacco – and some e-juice or vaping materials are nicotine free.
With vaping, the combustion process is minimized due to temperature controls the vaporizer has in place. By avoiding combustion, unlike traditional cigarettes, vaping has less chemical burn off.
If you can heat the active components enough to become diffused without causing the chemical combustion with the other compounds, you can get the feel-good dopamine effect without the damage of smoke inhalation.
The sensation between smoking and vaping is different as well. Depending on the type of vapor, vaping may feel wetter and heavier than cigarette smoke. Vapor appears thicker than smoke and disappears quickly into the air.
Many would also point out that it smells better than traditional tobacco cigarettes, too.
Is Vaping Healthier Than Smoking?
The answer for this is unclear, although many folks believe that since you’re inhaling vapor rather than smoke, vaping is the better and less hazardous option. The long list of harmful/toxic chemicals in traditional cigarettes gives the impression that vaping certainly can’t be any worse.
Due to the more recent emergence of vaping, the effects of long-term use can’t be defined with absolute certainty.
How Vaping Affects Health
Vaporizers administer nicotine with far less adverse effects due to fewer carcinogenic products and minimal smoke inhalation, but that does not necessarily mean vaping is good for you.
Evidence suggests that e-cigarettes can have toxins such as formaldehyde (carcinogen), nitrosamines (linked to cancer), and lead (neurotoxin). Propylene glycol, which is also used in theatrical smoke, is known to cause irritation to the eyes and respiratory infection.
A study from the American Association for the Advancement of Science suggests that vaping has a similar impact as cigarettes when it comes to suppressing the essential immune system-related genes.
Habitual users of e-cigarettes have a higher likelihood of oxidative stress and higher adrenaline in the heart than non-users. These two factors are risks associated with prominent heart disease.
While many birth control methods contain hormones, there are others that do not. Here are eight non-hormonal birth control options worth looking into.
Is Vaping Safer than Smoking?
Right now, this comes down to the difference between the documented harm of smoking and the presumption of less harm with vaping.
The risks involved with vaping are still uncertain, and we need more research in order to compare the two properly. It will be a long time before we have the full picture on the consequences of vaping; right now, we’re still piecing together bits of research.
Cigarettes went through a similar process, and the full implication on health became more known with each study over the course of decades.
For instance, there were a lot of people exposed to the harmful effects of cigarette smoke before the negative health implications were fully understood. Awareness of the effect of second-hand smoke came around long after smokers were aware of the health risks they were imposing on themselves.
The way regular cigarettes are made is well-known compared to vaping products that haven’t undergone the same amount of rigorous testing.
The risk of traditional smoking is well-documented, but research continues with the risk associated with vaping devices.
The Dangers of E-liquid
Substances used to create the e-juice can come with risk. Glycerine and propylene glycol can create carcinogens. If you vape, make sure you know the ingredients you’re directing to your lungs, because you may change your mind about the habit.
A study published by Tobacco Control suggests that levels of formaldehyde and metals have been found to be comparable to or higher than those found in conventional cigarettes.
Less harmful does not mean safe. Additives can contain other harmful chemicals, and second-hand smoke is still an issue. Exhaled particles from vaping, known as ultrafine particles, are known to affect pulmonary health.
It has been proven that smoking affects almost all parts of your body including:
- Destruction of alveoli (air sacs) in the lungs
- Inflammation in the airways and tissues of the lungs which leads to breathing issues
- Cancer risks
- Stress on the heart and blood pressure
- Sticky blood which is more likely to form clots and can lead to stroke or heart attack
- The buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries
- Lower estrogen levels
- Erectile dysfunction
- Weakened immune system
- Tired Muscles
- Hearing loss
- Increased risk of cataracts and macular degeneration
Is Vaping Harmful?
Vaping does lack some of the harmful ingredients in traditional cigarettes (like tobacco), but that doesn’t qualify it as risk-free.
Research has found that vaping indoors makes the air quality worse by increasing the concentration of nicotine, particulate matter, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and aluminum (linked to lung and heart disease, cancer, and other health effects).
Nicotine, which can be found in many vaping materials, can form a habit and dependence, not to mention it’s poisonous if ingested. Nicotine addiction is hard to beat because it alters your brain by developing extra nicotine receptors.
When you stop using nicotine, you go through withdrawal because your brain isn’t getting the nicotine to which it has become accustomed. Nicotine also affects brain development in young adults (since the brain is still forming). At very high levels, nicotine is toxic and potentially lethal.
We’re still decades away from seeing the long-term effects of vaping, but there are preliminary studies that show the hazards involved.
How Vaping Can Affect Your Lungs
It’s no surprise that smoking is toxic to your lungs: it causes inflammation, scar tissue, emphysema, makes you more susceptible to respiratory infections and more.
As for vaping, it has been suggested in a study by the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine that vaping products can trigger potentially harmful immune responses in the lungs.
In the study, they found higher levels of unique immune proteins that were not witnessed in the smokers and non-smokers that also took part in the study. If levels of these proteins are constantly high, there is a risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The sort of lung inflammation may potentially mean that vaping can be a risk factor for cancer, but long-term research is required before this hypothesis can be given any weight.
Vaping to Quit Smoking – Does it Work?
The idea that vaping is a stepping stone on the way to helping smokers quit cigarettes has helped some folks but may not be the way to quit cigarettes entirely.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse cites statistics that 31 percent of vaping device users started smoking within six months, compared to 8 percent of non-users.
Trying to cut back on traditional cigarettes and introduce vaping into your life at the same time may minimize the number of cigarettes you smoke but using both products at the same time means many traditional smokers never actually quit.
Vaporizers and E-cigarettes are not FDA-approved devices for quitting smoking as NRTs (nicotine replacement therapies), because of the lack of both research and regulation.
Vaping and Youth
Vaping also has the opposite effect than intended. There has been an increase in vaping and e-cigarettes amongst middle and high school students.
With the fun, dessert-mimicking flavors and novelty appeal of vaping, it can seem marketed toward youth and may introduce younger generations to cigarettes without intention. This is especially problematic as the trend isn’t understood by a large percentage of this age group and they are unaware of ingredients, how vaping works, and what it does to their health.
The World Health Organization reports that vaping can become a gateway to smoking. If kids are starting young, there could be some health implications down the road.
The Bottom Line
Long story short, if you’re a non-smoker who doesn’t vape, don’t start. The question mark surrounding the long-term health effects isn’t worth it.
Smoking is a leading cause of preventable deaths in developed countries; theoretically, vaping would have to be pretty bad to be considered worse than smoking, but is it worth the risk?