What Is Bronchitis?
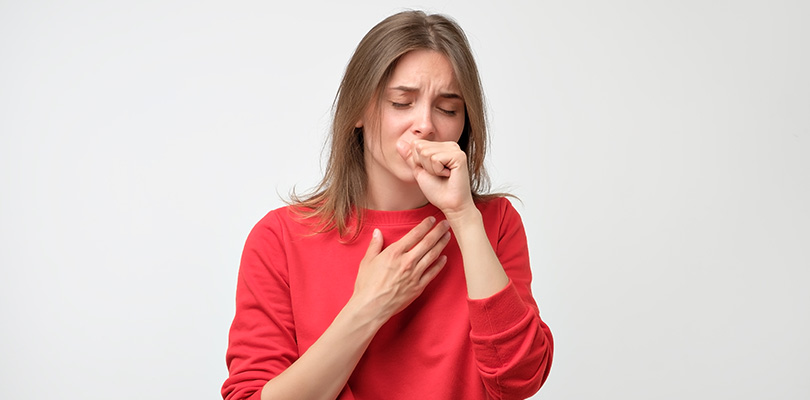
Bronchitis is a health condition that causes bronchial tubes, the airways responsible for transporting air to your lungs, to swell. Bronchitis arises due to infection or irritation of the bronchial tubes by viruses, bacteria, and many other microbes and particles. People with bronchitis experience breathing problems and difficulties in eliminating heavy mucus from their airways.
Bronchitis falls into two categories: acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis. Acute bronchitis is a brief illness that usually presents after a viral infection or cold, while chronic bronchitis is a long-term illness triggered by prolonged illness or environmental factors.
In this article, we’ll give a brief overview of bronchitis, discuss the transmission of the infection, and highlight some home remedies you can try if you come down with a case of bronchitis.
Bronchitis Symptoms
A persistent cough that persists for several weeks to a couple of months is one of the most common symptoms of bronchitis. Symptoms of chronic bronchitis tend to flare several times per year and are usually more severe during the winter months.
Bronchitis may also cause breathing difficulties, including chest congestion, shortness of breath, a cough that produces a lot of mucus, and a whistling or wheezing with breathing. Other symptoms of bronchitis may include:
- Low-grade fever and chills.
- Headaches.
- Sinus pain and nasal congestion.
- Sore throat.
How Will You Know You Have Bronchitis?
It’s difficult to differentiate a regular cold from bronchitis within the first couple of days of symptoms. However, if your cough persists for more than a week, and you develop other common symptoms of the infection, this may be an indication that you have bronchitis.
How Long Does Bronchitis Last?
Acute bronchitis often lasts for approximately 10 to 20 days, with the cough persisting for five days or longer.
Individuals with frequent acute bronchitis episodes have a higher risk of developing chronic bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis causes a cough accompanied by sputum production that happens daily and lasts for not less than three months in two consecutive years.
Is Bronchitis Contagious?
Acute bronchitis is contagious because cold or flu viruses that are contagious are responsible for the infection.
On the other hand, chronic bronchitis isn’t contagious; however, it’s a complex health condition that requires professional help. It develops due to exposure to things like chemicals, dust, or smoke from cigarettes or fire that cause irritation to the lungs.
How Long Will You Be Contagious?
The duration of your contagiousness varies with the type of virus that triggered your bronchitis. In most instances, you will be infectious for a couple of days to a week. Given that you may not be familiar with the type of virus that has infected you, it’s safe to assume you can transmit the infection once cold symptoms begin.
Vitamin B12 helps to support adrenal function, maintain a healthy nervous system, caring for your skin and hair, and critical for proper bodily function.
How Is Bronchitis Transmitted?
The process of acute bronchitis transmission is similar to cold or flu viruses. Viruses are released into the air, and on surfaces, when a sick person sneezes, blows their nose, coughs, or breathes. The virus is then transferred into your body through your eyes, nose, or mouth.
Is Bronchitis Contagious Through Kissing?
Kissing is one way of transmitting acute bronchitis. Since this type of bronchitis involves persistent coughing, it can generate lots of mucus that mixes with the saliva.
The viruses that are responsible for causing acute bronchitis to travel through the respiratory mucus, therefore, when you exchange saliva with a person infected with acute bronchitis, it’s likely that you will get the infection.
Is Bronchitis Contagious Even When You Are Taking Antibiotics?
Your level of contagiousness will start to dwindle within 24 hours if starting antibiotics. After a couple of days of antibiotic treatment, you will not be infectious at all.
Is Bronchitis Treatable at Home?
There are a variety of home remedies available that may be helpful in alleviating symptoms and making you more comfortable while you recuperate from bronchitis, including:
- Getting enough sleep and taking a break from your regular routine to allow your body time to rest and recover.
- Drinking lots of fluids such as water, chicken soup, and tea.
- Taking over-the-counter pain medicine to minimize pain and ease discomfort.
- Consulting your doctor concerning the kind of cough medication you should take. Certain over-the-counter cough medicines
reduce coughs but make it difficult for you to get rid of mucus. However, they can help you get sufficient sleep. Conversely,
other cough medications are expectorants that help you get rid of mucus, but they interfere with your ability to sleep. - Avoiding cigarette smoke, secondhand smoke, and air pollutants.
- Using herbal supplements like garlic or ginger to reduce discomfort in the bronchial airways and encourage healing.
What Are the Risk Factors for Bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis shares similar risk factors with viral and bacterial infections.
Being within close proximity to people that are sneezing, blowing their noses, coughing, and touching objects recently handled by infected persons increases your risks of getting bronchitis.
Other risk factors for bronchitis include exposure to tobacco smoke, aerosolized chemicals, and air pollution.
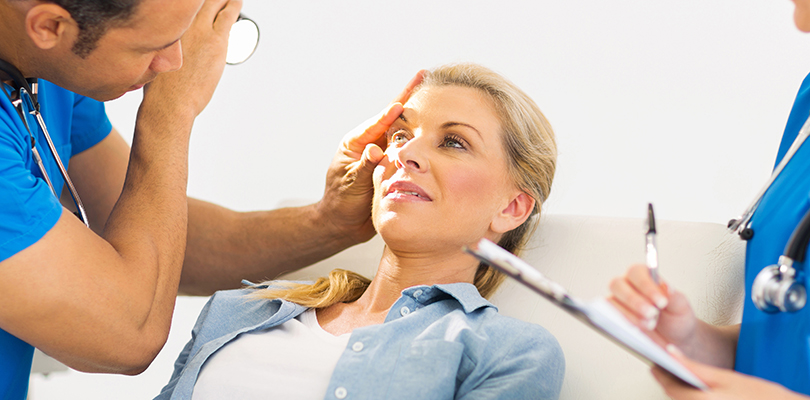
When Should You See a Doctor?
Acute bronchitis will clear up on its own, but you should consult your doctor if you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms:
- Recurrent episodes of acute bronchitis, as this may be an indication of the onset of chronic bronchitis.
- Wheezing or a persistent cough that persists for more than a month.
- Coughing that emits blood or bloody mucus.
- Symptoms that worsen.
- Shortness of breath.
Since flu viruses are responsible for causing certain episodes of acute bronchitis, your doctor may recommend antiviral drugs, especially when the suspected causative age is the flu virus.
Bronchitis can result in pneumonia and other serious complications, so it’s imperative to seek medical assistance if symptoms are severe or if they persist.
Conclusion
In most cases, acute bronchitis goes away on its own within a few weeks. Getting enough rest and staying adequately hydrated during this period is essential to encourage healing.
Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, is incurable and treatments for this health condition concentrate on alleviating the symptoms rather than curing the infection. Making lifestyle changes such as consuming a healthy diet, working out regularly, and avoiding cigarettes and pollution can be instrumental in easing symptoms of chronic bronchitis and improving your quality of life.